Using Visual Tools to Manage Your Team, Department, or Organization
I am excited as we have rolled out our new Daily Management System and Portland Bottling Company., As a manager in the beverage industry, it’s essential to have a clear and concise visual management system in place. This system should be updated regularly with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to ensure that everyone on the team is on the same page. The purpose of a visual management board is to provide everyone with a comprehensive overview of the business’s performance and to promote transparency and accountability, and teamwork.
In this blog post, we will be discussing how we updated our visual management board with KPIs, and how we got our hourly team members and operators involved in the process.
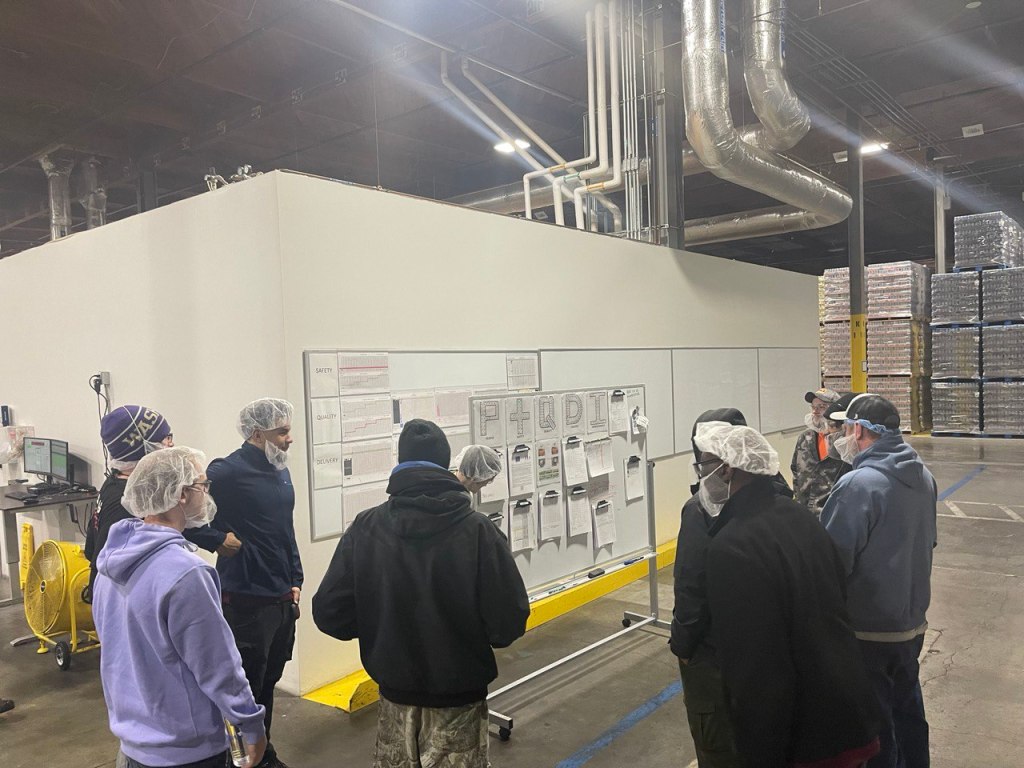

Step 1: Identifying the Key Performance Indicators
The first step in updating our visual management board was to identify the KPIs that would be the most impactful for our team. We considered a range of factors, including production efficiency, product quality, and customer satisfaction, to determine which KPIs would be the most relevant. All team members got to weigh in on the discussion. The critical point is that if your hourly team members are going to “own” the board, they have to be involved in the creation process.
Step 2: Setting Up the Visual Management Board
We chose to go with a basic board but with a twist or two on it.
- Since we truly believe that our People are our greatest asset – that KPI comes first.
- Secondly, we chose Safety as that easily coincides with taking care of our team members and ensuring compliance with training requirements.
Step 3: Involving the Hourly Team Members and Operators

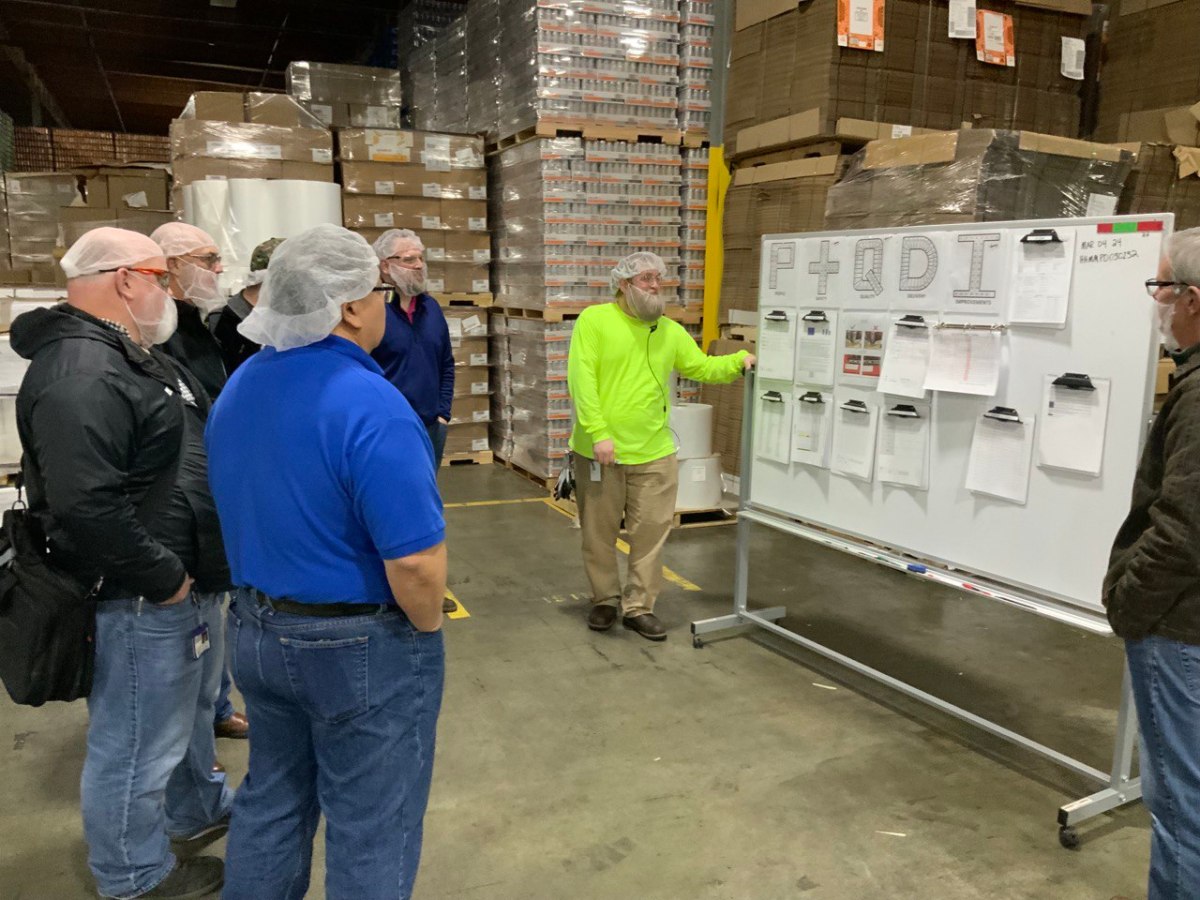
Once we had identified some of the KPIs, we set up a visual management board in our production office area. We held multiple training sessions with multiple departments and even enjoyed “mock” meetings where we got to do a meeting and offer feedback and support to each other. It actually turned out to be quite fun.
The next step was to get our hourly team members and operators involved in the process. We organized a team meeting and invited everyone to discuss the new visual management board. During the meeting, we explained the purpose of the board and how the KPIs would be used to improve production efficiency and customer satisfaction. We also invited everyone to suggest additional KPIs that they believed would be beneficial.
As we implemented the system live, the boards were placed as close to the machines as possible, where they could be easily seen by everyone on the team. We used color-coded charts and graphs to display the KPIs, which made it easy for everyone to understand the data.
Step 4: Updating the Visual Management Board Regularly
We updated the visual management board regularly, ensuring that the KPIs were accurate and up-to-date. This allowed everyone to track their performance and make improvements where necessary. We also provided regular feedback to our hourly team members and operators on their performance and how they were contributing to the overall success of the business.
Step 5: Celebrating Success
Finally, we celebrated success by recognizing the achievements of our hourly team members and operators. This helped to promote a positive and motivated work environment, and it encouraged everyone to continue working towards our shared goals.
Step 6: Management Gemba Walks
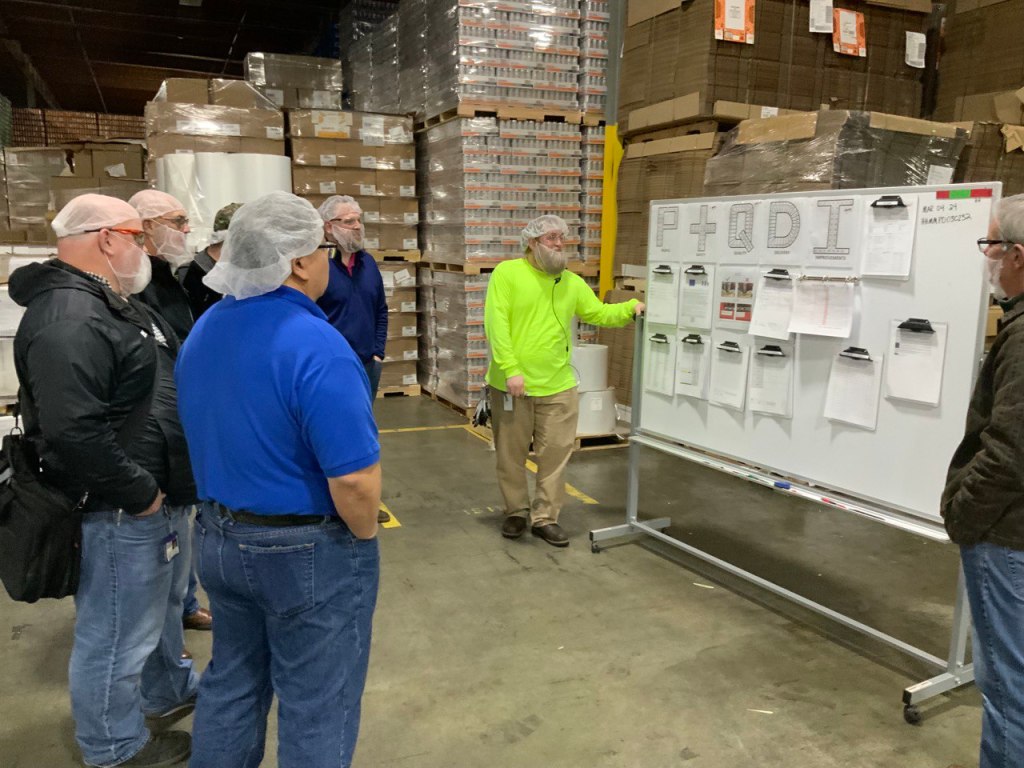

Don’t forget about your Management Gemba Walks.
The purpose of management Gemba walks in a visual management system is to enable managers to observe and evaluate how work is being performed in the workplace. Gemba is a Japanese term that means “the real place” or “the place where work is done.” Gemba walks are a management technique that involves going to the actual location where work is being performed, observing the process, and talking to the employees who are performing the work.
In the context of a visual management system, Gemba walks allow managers to see how the system is functioning in practice, identify any issues or problems, and make necessary improvements. Visual management systems are designed to make information about processes, performance, and quality visible and easily understandable, so Gemba walks can be used to ensure that the information being presented is accurate and up-to-date.
Our managers do their formal Gemba twice a week to observe as close to the machine as possible. By actively engaging with employees and observing the process in action, managers can gain a deeper understanding of how work is being done, identify any inefficiencies or areas for improvement, and provide feedback to the team. Gemba walks also provide an opportunity for managers to build relationships with employees, demonstrate their support for the team, and reinforce the importance of continuous improvement
In conclusion, updating our visual management board with KPIs has been a valuable process. It has helped us to promote collaboration, teamwork, and a shared understanding of our goals. By involving our hourly team members and operators in the process, we have been able to improve production efficiency, product quality, and customer satisfaction.